
If given the equation in standard form, you may need to complete the square and transform the equation to the graphing form in order to graph the circle.
Given the equation of a circle in standard form, x2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0, here’s an example of completing the square to transform the equation to graphing form:
| x2 – 6x + y2 + 2y – 26 = 0 | Given this equation in standard form where A = 1, B = 0, C = 1, D = -6, E = 2, F = -26. |
| (x2 – 6x + ___ ) + (y2 + 2y + ___ ) = 26 + ___ + ___ | Fill in the blanks with the numbers that will complete the squares for each variable, x and y. Move the constant (F) to opposite side of equation. |
| (x2 – 6x + 9) + (y2 + 2y + 1) = 26 + 9 + 1 | Be sure to add the same values to both sides of the equation. |
| (x – 3)2 + (y +1)2 = 36 | Write the perfect squares in factored form and simplify the right side of the equation. |
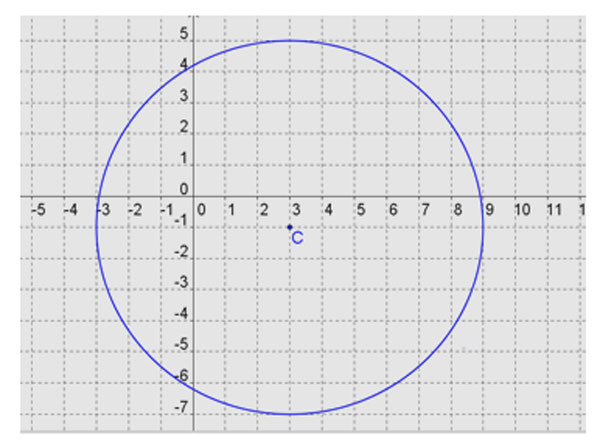
This will reveal the values of h, k, and r. In this case, h = 3, k = -1, and r = 6. So this circle has center (3, -1) with radius 6.
Go to Print Free Graph Paper or use your own graph paper to sketch the graph of this circle.
Now you transform the following two equations and find the values of h, k, and r in order to graph each circle. Then graph each on your own graph paper. Click the blanks below to see the correct answers.
x2 - 8x + y2 + 10y + 5 = 0
h = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ 4
k = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ -5
r = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ 6
x2 + y2 - 12y - 13 = 0
h = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ 0
k = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ 6
r = Interactive button. Assistance may be required. ______ 7