

You will learn how to solve a quadratic inequality using algebraic methods and then represent your solution.
Just like you do when you are looking at graphs of quadratic inequalities, the best practice is to use the standard form of a quadratic equation. This will enable you to solve the quadratic inequality algebraically just as you would solve a quadratic equation, and then you can find the solution set for the given inequality.
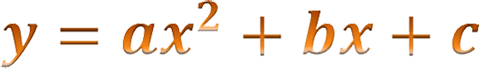
Recall that as you graphed the solutions to quadratic inequalities, you were shading the region of the graph that satisfied the inequality. To be more precise, you are shading the region that represents the values of x that satisfy the inequality. What happens when you are solving the inequality without graphing?
To answer this question, consider what actions you had to take to solve the linear inequality, 10 < 2x + 4 algebraically.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.10 < 2x + 4
First, you would subtract 4 from both sides.
10 − 4 < 2x + 4 − 4
6 < 2x
This would leave you with 6 is less than 2 times x.
6 < 2x
Next, you would divide both sides by 2.
6 over 2
6
2
<
2x over 2
2x
2
3 < x
This would leave you with 3 is less than x.
3 < x
Your solution set is any value of x that is less than 3. Another way to read this solution would be that 3 is greater than any value of x.

After using inverse operations, you ended up with the solution, 3 < x. However, you still need to represent the solution set on the number line. Recall that this is where you had to determine whether or not 3 is part of the solution. You also need to determine whether the point, 3, is represented by a closed or open circle.
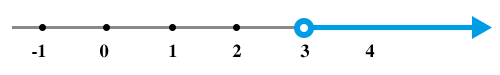
You will find the root or roots of the quadratic. You will then create a sign chart and test values of x using the inequality. At that point, you will be able to represent the solution of a quadratic inequality on a number line.