In this section, quadratic equations with non-integral solutions are examined.
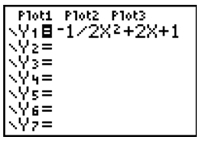
Example: Solve: - one-half 1 2 x2 + 2x + 1 = 0
Step 1: Enter the equation into [Y=].

Step 2: Go to the table.
Step 3: Use the up and down arrows to scroll up and down the table.
Between what x-values does -
1
2
x2 + 2x + 1 = 0
How did you determine where the solutions were located?
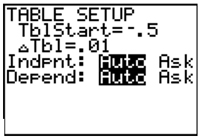
Step 4: Once you have narrowed down where the solution is located, you can examine the values between these numbers by changing the table interval in the TABLE SETUP window. Go to [2ND] [WINDOW].
Step 5: Change the table interval to tenths.
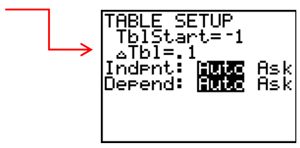
Step 6: Now, go back to the table. Between what x-values does - 1 2 x2 + 2x + 1 = 0?
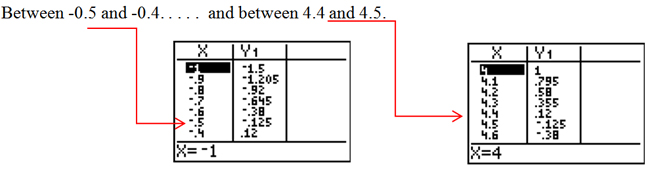

Now see if you can round to the nearest hundredth.
Hint: Since you know that the zero is between -0.5 and -0.4, enter one of these numbers for TblStart. This will reduce the amount of scrolling needed.