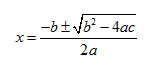
Another method for solving a quadratic equation is to use the quadratic formula. To use the formula, the equation must be in the standard form of a quadratic equation. The formula is shown below.
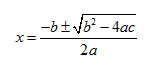
x2 + 6x = 4
x2 + 6x – 4 = 0
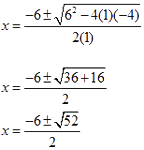
x ≈ -6 ± 7.21 2 numerator: -6 +- 7.21, denominator: 2
x ≈ -6 + 7.21 2 numerator: -6 + 7.21, denominator: 2 or x ≈ -6 – 7.21 2 numerator: -6 - 7.21, denominator: 2
x ≈ 0.605 x ≈ -6.605
The first step is to put the quadratic equation in standard form.
Identify the values of a, b, and c and use these values in the formula. a = 1, b = 6, c = -4
Begin simplifying by performing the operations under the square root.
Finish simplifying the expression.
Approximate √52square root of 52 to the nearest hundredths.
The solutions to the equation are approximately 0.605 and -0.605.
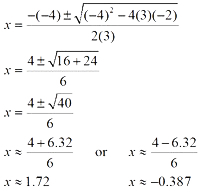
3x2 – 4x – 2 = 0
The equation is already in standard form. Identify a, b, and c: Use these values in the quadratic formula.