
In this section, rational function models are used to solve mixture problems. A graphing calculator is needed.
Have you ever looked into a mirror to see your reflection? Have you ever stood away from a mirror and seen how light from elsewhere in the room gets reflected in the mirror to shine somewhere else?
Use the linked light bounce applet for each of the problems below. This tool simulates bouncing a laser light beam into a mirror that is sitting on top of a block 10 cm above the floor and onto the wall. You are allowed to move the distance the mirror is from the wall, the height of the laser above the floor, and the distance the laser is from the wall.
In the following activities, the height of the reflection on the wall is a function of the pointer’s distance from the wall.
Adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, is 100 cm from the wall and the pointer is 225 cm above the floor (the red point horizontally across from P). Drag point P to the following distances and record the height of the reflection on the wall on a piece of paper to complete a table similar to the one shown below and then construct its graph.
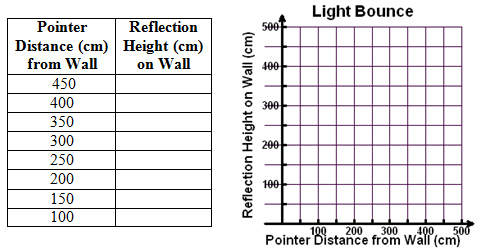
The data and graph of this situation can be modeled with a rational function having the equation
y =
k over x - d
k
x − d
+ m
where m is the height of the mirror above the floor and d is the distance between the mirror and the wall. The variable k is the constant of variation and is found by solving the equation for k after substituting in the values of m and d and using the coordinates of a selected point (x,y).
Select one of the points from your table and find the equation for this situation.
Verify your equation by typing it in y = on your graphing calculator and checking that the table values match those in the table above.y = twenty-one thousand six-hundred over x minus one hundred 21600 x − 100 + 10

Adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, is 100 cm from the wall and the pointer is 150 cm above the floor (the red point horizontally across from P). Drag point P to the following distances and record the height of the reflection on the wall. Complete a table similar to the one below and construct its graph on your own paper.

Remember, the data and graph of this situation can be modeled with a rational function having the equation
y =
k over x - d
k
x − d
+ m
Find the equation for this situation and verify your equation in the graphing calculator.
Activity 3: Adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, is 50 cm from the wall and the pointer is 150 cm above the floor (the red point horizontally across from P). Drag point P to the following distances and record the height of the reflection on the wall. Complete a table similar to the one below on your own paper.
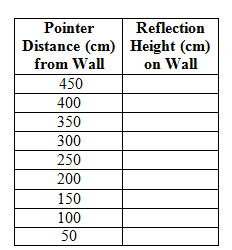
Find the equation for this situation and verify your equation in the graphing calculator.