 The Light Bounce applet below displays the range of the reflection of a beam of light initiating from a laser pointer above the ground reflecting off a mirror on the floor to a spot on a wall.
The Light Bounce applet below displays the range of the reflection of a beam of light initiating from a laser pointer above the ground reflecting off a mirror on the floor to a spot on a wall.
![]()
 The Light Bounce applet below displays the range of the reflection of a beam of light initiating from a laser pointer above the ground reflecting off a mirror on the floor to a spot on a wall.
The Light Bounce applet below displays the range of the reflection of a beam of light initiating from a laser pointer above the ground reflecting off a mirror on the floor to a spot on a wall.
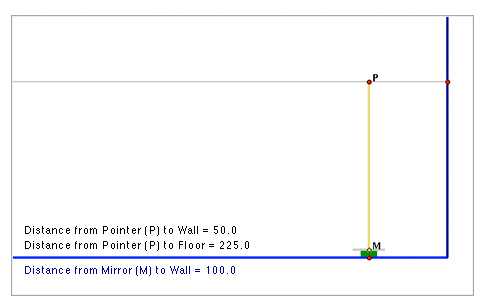
Adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, is 100 cm from the wall, the red dot on the vertical line above R is 225 cm above the floor.
Answer the questions below on your own paper or in your notes. Once you have answered the questions, click on Check Your Answer.
Source: Light Bounce, NCTM Illuminations
When you adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, was 100 cm from the wall and the pointer was 225 cm above the floor, the equation relating the height of the reflection on the wall as a function of pointer distance from the wall is:
y =
twenty-one thousand six-hundred over x minus one hundred
21600
x − 100
+ 10
The vertical asymptote is x = 100. It is the result of the mirror being 100 cm from the wall. If the laser is directly above the mirror, the light reflects back at the laser and not at the wall.

The horizontal asymptote is y = 10. It is the result of the mirror being 10 cm above the floor. This applet does not allow us to change the height of the mirror.


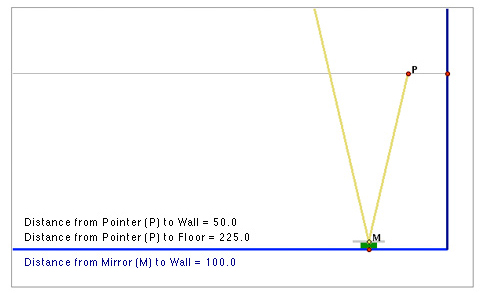
When the laser pointer is 50 cm from the wall, that is between the mirror and the wall, its reflection bounces away from the wall. That is why there is no "Height of Reflection" value shown above.

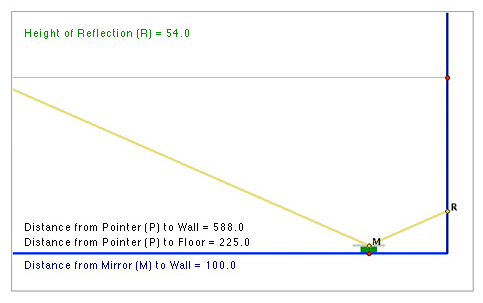
588 cm is the farthest this applet moves the laser point. There is no distance from the wall and at 225 cm above the floor where there would be a reflection of light on the wall of 5 cm. Since the mirror is already at a height of 10 cm above the floor, there cannot be a reflection that is below that height.

Two different reflections: If you adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, remains 100 cm from the wall but move the height of reflection to 150 cm above the floor. The equation relating the height of the reflection on the wall as a function of pointer distance from the wall is y = fourteen thousand over x minus one hundred 14000 x − 100 + 10
If you adjust the tool so that the mirror, M, is 50 cm from the wall, keep the height of reflection 150 cm above the floor, the function is y = seven thousand two hundred over x minus fifty 7200 x − 50 + 10
The equation for Activity 2 was y = fourteen thousand over x minus one hundred 14000 x − 100 + 10 and for Activity 3 was y = seven thousand two hundred over x minus fifty 7200 x − 50 + 10.
All three equations include a +10, the horizontal asymptote for all three because the mirror's height above the floor remained 10 cm for all of them. The vertical asymptotes of the first two activities and the third are different because the mirror was at different distances from the wall during the two activities. In Activity 1 and 2, the mirror was 100 cm from the wall so its vertical asymptote is x = 100. In Activity 3, the mirror was 50 cm from the wall so its vertical asymptote is x = 50.

There are different "k" values because the laser pointer is at different heights from the floor or because the mirror is at a different distance from the wall. In the activities the mirror and the distance the pointer is to the floor are the following: Activity 1 – 100 cm/ 225 cm, Activity 2 – 100 cm/150 cm, Activity 3 – 50 cm/ 150 cm. These distances created different reflection heights for the same laser distances therefore there has to be different constants of variations.

In Activity 3, the mirror was 50 cm from the wall so all the distances from the wall for the laser pointer had to be greater than that. The domain is x > 50. The mirror was set on a block 10 cm above the floor so all of the reflections had to be a height higher than that since the laser light was coming from above the mirror. The range is y > 10.

Write a word problem that can be modeled by a rational function and create the equation to model the situation. State the vertical and horizontal asymptotes and how they fit the situation, if possible. Then, describe the domain and range for your situation. (Remember, the graphs of the equation may be different from the graph of the situation because values in the domain of the equation may not make sense for the situation.)