Source: Scientific Method, Science Buddies

Source: Scientific Method, Science Buddies
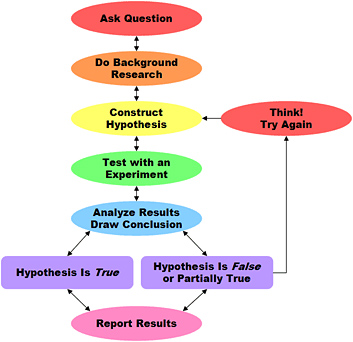
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observable phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be used in science, one must be able to test it in the form of an experiment. The hypothesis is not just an "educated guess". Usually hypotheses are based on previous observations that can't be explained with available information. Referring back to the diagram of the scientific method, the previous steps of "Ask a Question" and "Do Background Research" are designed to help express the problem in a single question and propose an answer to the question based on what you know. The experiment is designed to test this hypothesis.
If one asked the question "Is it true that earthworms prefer to be in dark places?" then a valid hypothesis might be, "If sunlight harms earthworms and earthworms are put in the sunlight, they will crawl to a dark place."
A hypothesis is supposed to address causes that lead to effects. The suggested cause is the hypothesis; the expected effect or result is the prediction. In the statement above, identify the hypothesis and the prediction. Click below for help.
Hypothesis: Sunlight harms earthwormsThe process of forming a hypothesis is designed to produce testable predictions. The test is the experiment. The hypothesis is the statement of cause and effect that drives the design of the experiment.
An example of a formal scientific hypothesis would be: "IF plants need fertilizer to grow AND we apply fertilizer to some plants THEN those plants should grow taller than plants that were not given the fertilizer." The IF section is the hypothesis, the AND section is the basis for the experiment, and the THEN section is the prediction. This hypothesis only addresses one factor of plant growth which is ok. From this experiment and its results, more questions may be raised and further experiments may be done.
Now it is your turn: Write a formalized scientific hypothesis using the earthworm example from above.
Could be anything reasonable. Ex. IF sunlight harms earthworms, AND they are given a choice between a light and dark environment, THEN they will crawl to a dark place. Close