The word prokaryote comes from the Greek roots pro, which means “before” and karyose, which means “kernel.” In biology this word root is referred to as the nucleus of a cell. Therefore, prokaryotic means "before a nucleus." Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane bound nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is in a circular loop in a region referred to as the nucleoid. (Nucleoid means nucleus-like.) Members of the kingdoms Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria) and Eubacteria (true bacteria) are prokaryotic.
![]() Let's look at a prokaryotic cell (bacteria cell) more closely.
Let's look at a prokaryotic cell (bacteria cell) more closely.
Directions: Scroll over the letters to view the name of the structure and the function. Take notes on the structure and function of the parts of this prokaryotic cell.
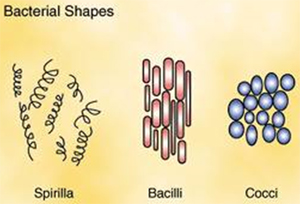
This interactive showed a typical prokaryotic cell. There is variation found in prokaryotes. For example, most bacteria come in one of three basic shapes: spirilla, bacilli, and cocci. As you can see in the picture below, spirilla are spiral shaped, bacilli are rod shaped, and cocci are round.
Sources for images used in this section as they appear top to bottom: