
You have just demonstrated how DNA and RNA can affect the outcome of cell differentiation, but it is also important to know that gene expression can be influenced by environmental factors. For example, available nutrients, salinity, and temperature can influence gene expression in organisms. In E. coli bacteria, the lac operon gene is only turned on when the bacteria are using lactose as a primary food source.
Another example of environmental factors influencing gene expression is metamorphosis. Metamorphosis is regulated by external and internal factors, including temperature, available resources, and hormones. For example, a tadpole in a pond will go through many physical changes as it responds to the environment. Environmental conditions trigger hormone release that allows the tadpole to create new specialized cells so that it can survive in its environment.
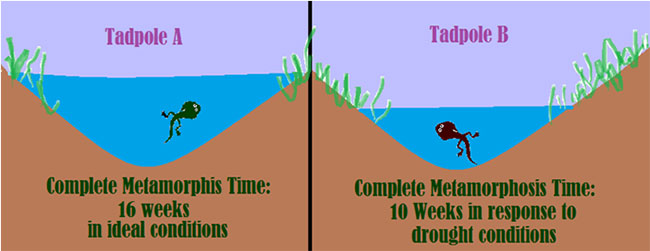
Look at the pictures below. The tadpole in Figure A will spend about 16 weeks of its life undergoing metamorphosis before becoming an adult frog. The cells of the tadpole in Figure B, living in an area of drought with less water, will release hormones to speed up the process of metamorphosis in response to its environment. Both tadpoles will survive to become adult frogs, but their cell differentiation is being controlled at different rates.
Sources for image used in this section: