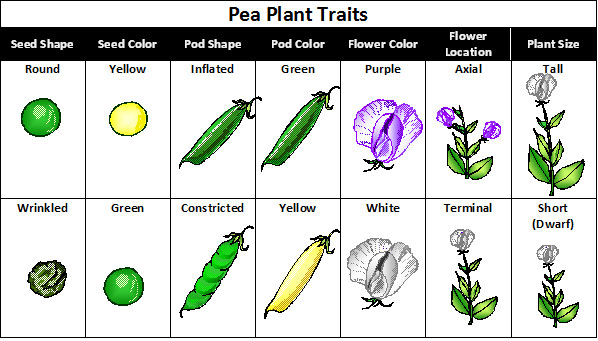
Mendel studied seven traits of pea plants. He noticed that each of these seven traits had two contrasting characteristics.

Mendel followed the principles of experimental design and only tested one trait at a time during his experiment. This helped him control the factors of his experiment to keep more than one variable from being tested with each experiment.
![]() Let’s look at Mendel’s experiment and the results he had.
Let’s look at Mendel’s experiment and the results he had.

Source: Mendel’s notes, Mendel Museum
For eight years, Mendel performed over 28,000 crosses with the pea plants. Mendel kept accurate records of all his experiments. The image to the right shows a page of Mendel’s notes.
In 1866, Mendel published a paper describing his experiments and conclusions.
Mendel made the following three important conclusions, which still hold true to date:
Mendel’s work was not recognized at the time he published his paper. In 1900, long after Mendel died, his results were rediscovered and verified. Gregor Mendel is now considered the father of genetics.