
Source: Penny, Matthiasxc, flickr
You have studied probability in math class. Probability is important in the study of genetics. When studying heredity, geneticists want to know the probability, or likelihood, of particular traits being passed on to offspring.

Source: Penny, Matthiasxc, flickr
Let’s look at probability a bit closer.
Have you ever flipped a coin to make a decision? When you flip the coin, what is the probability of the coin landing on heads?
The probability of a single event can be calculated using the following formula:
Probability = Number of favorable outcomes over Total number of possible outcomes Number of favorable outcomes Total number of possible outcomes
A favorable outcome is the outcome of interest. When answering the question, what is the probability of the coin landing on heads, the number of favorable outcomes would be one. There are two possible outcomes, heads or tails. The probability of the coin landing on heads would be 1 over 2 1 2 or 50 percent. The probability could also be written as a ratio of 1:2 (one out of two).
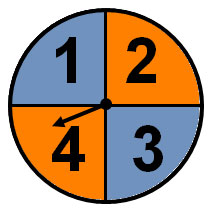
Here is another example.
What would be the probability of the spinner landing on the number four?
In this problem, there is still one favorable outcome, but now there are four total possible outcomes. So, the probability of the spinner landing on the number four would be 1 over 4 1 4 or 1:4 or 25 percent.
What is the probability that the spinner would land on orange?
Since there are two areas that are colored orange, the number of favorable outcomes would be two. There are four regions on the spinner, so the total number of possible outcomes is four. The probability of the spinner landing on an orange colored region would be 2 over 4 2 4 , which can be reduced to 1 over 2 1 2 . The probability could also be written as 50 percent. If asked for the ratio, the probability would be 2:4 or 1:2.
When Mendel crossed two plants that were heterozygous for stem height, he noticed that most of the offspring were tall and a few where short. Mendel kept detailed records of his experiments. When he analyzed his data, he realized that probability could be used to explain the results.
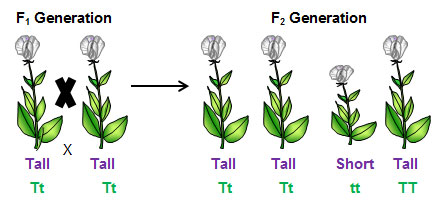
When two plants that are heterozygous for stem height are crossed, what is the probability of an offspring having a tall stem?