
Source: Brown and tan mice, Scientific American
Complete the following practice problems. There are six steps to completing a monohybrid cross.

Source: Brown and tan mice, Scientific American
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dominant allele: B=brown

Source: Radish Roots, Crop Genebank Knowledge base
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dominant allele: B=bent

Source: Hairline shape, groovy post
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dominant allele: W=widows peak
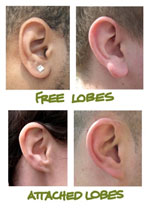
Source: earlobe attachment, Human anatomy for the artists
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dominant allele: F=free ear loves
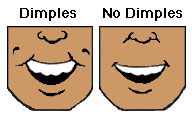
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dominant allele: D=dimples