
Source: Gray and White rabbit, Common Places.com
Complete the following practice problems. There are six steps to completing a dihybrid cross.

Source: Gray and White rabbit, Common Places.com
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Fur Color:

Source: Guinea Pigs, Pets 4 homes and Pet Mania
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Fur Texture:

Source: Hairline shape, Groovy Post
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
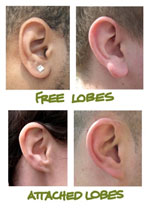
Hairline:
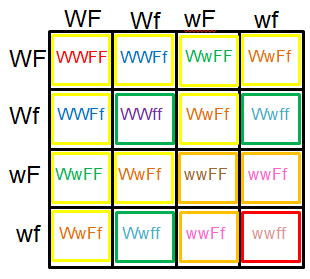
| Hairline: Dominant allele: W=widow's peak Recessive allele: w=straight Earlobes: Dominant allele: F=free earlobes Recessive allele: f=attached Cross: WwFf x WwFf Genotypes: Genotypes: 1 over 16 1 16 WWFF 2 over 16 2 16 WWFf 2 over 16 2 16 WwFF 4 over 16 4 16 WwFf 1 over 16 1 16 WWff 2 over 16 2 16 Wwff 1 over 16 1 16 wwFF 2 over 16 2 16 wwFf 1 over 16 1 16 wwff Phenotypes: 9 over 16 9 16 Widow's peak and free earlobes 3 over 16 3 16 Widow's peak and attached earlobes 3 over 16 3 16 Straight hairline and free earlobes 1 over 16 1 16 Straight hairline and attached earlobes |
 |

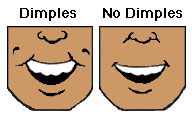

Source: Fun Experiments, Michigan Reach Out
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Dimples: