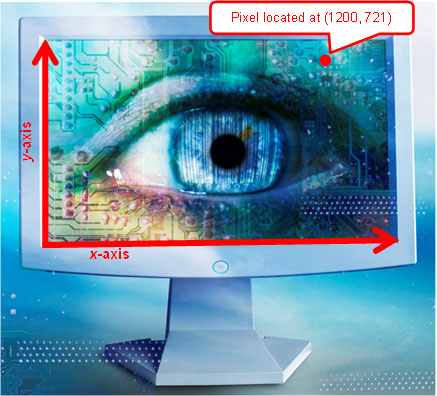
A common application of coordinate dilations is displaying digital images on a computer monitor.
A computer monitor, or computer screen, contains a certain amount of pixels. A pixel is a point on the monitor that lights up with a particular color, depending on the program that is being run.

Pixels are given a location using Quadrant I of a coordinate plane. Computer programs use x- and y-coordinates to locate each pixel and assign it a particular color.
For example, the monitor shown in the picture has a horizontal dimension of 1366 pixels and a vertical dimension of 768 pixels. Each pixel on the monitor can be used to generate an image.
The pixel shown is 1200 pixels from the left-hand corner, or origin, and 721 pixels above the left-hand corner, or origin. It is the pixel located at the ordered pair (1200, 721).
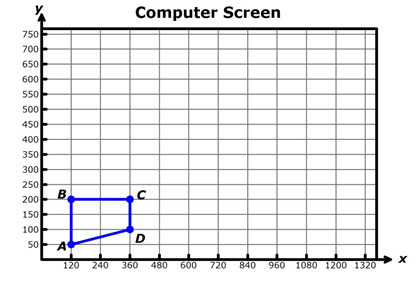
Let’s see this in action. Adan is a computer programmer, and he wants to generate an animation sequence by enlarging a figure whose outline is the trapezoid shown on the graph below. He is using a computer monitor like the one shown before, with a horizontal dimension of 1366 pixels and a vertical dimension of 768 pixels. His computer screen and the outline of the image are shown on the graph below.

![]() First, let's practice with the following activity using scale factors to identify new coordinates. The slider on the left hand side changes the scale factor.
First, let's practice with the following activity using scale factors to identify new coordinates. The slider on the left hand side changes the scale factor.
Use the information from the graph to fill in the chart below.
|
|
|||||
Point |
Original Coordinates |
Scale factor |
Scale factor 1.5 |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
|
|
|||||
Point |
Original Coordinates |
Scale factor |
Scale factor 1.5 |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
A |
(1,1) |
(1,1) |
(1.5,1.5) |
(2,2) |
(2.5,2.5) |
(3,3) |
B |
(2,5) |
(2,5) |
(3,7.5) |
(4,10) |
(5, 12.5) |
(6,15) |
C |
(4,1) |
(4,1) |
(6,1.5) |
(8,2) |
(10,2.5) |
(12,3) |

Study the table you created. Describe how the scale factor can be used to determine the new coordinates.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required. The new x and y coordinates can be found by multiplying the original coordinates by the scale factor.

Now that you practiced finding the coordinates using scale factors, go back to the graph showing the outline of the image Adan would like to enlarge.
Copy the table below in your notes, and fill in the blanks.
|
New Coordinates |
||||
Point |
Original Coordinates |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
A |
(120,50) |
|
|
|
|
B |
(120,200) |
|
|
|
|
C |
(360,200) |
|
|
|
|
D |
(360,100) |
|
|
|
|
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
|
New Coordinates |
||||
Point |
Original Coordinates |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
Scale factor |
A |
(120,50) |
(180, 75) |
(240, 100) |
(300, 125) |
(360, 150) |
B |
(120,200) |
(180, 300) |
(240, 400) |
(300, 500) |
(360, 600) |
C |
(360,200) |
(540, 300) |
(720, 400) |
(900, 500) |
(1080, 600) |
D |
(360,100) |
(540, 150) |
(720, 200) |
(900, 250) |
(1080, 300) |

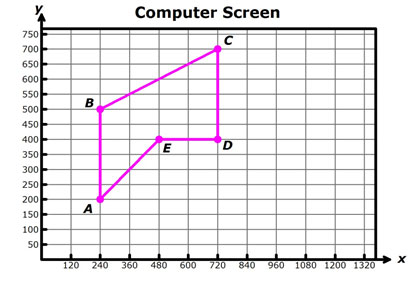
Pentagon ABCDE is the outline of a figure on a computer screen. The pixels representing the vertices of the pentagon are shown below.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Use the points to read the coordinates of each labeled point, and then use the scale factor to determine the coordinates of the new pixel. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
A' (144, 120), B' (144, 300), C' (432, 420), D' (432, 240), and E' (288, 240)
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
A' (144, 120), B' (144, 300), C' (432, 420), D' (432, 240), and E' (288, 240)

Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Use the points to read the coordinates of each labeled point, and then use the scale factor to determine the coordinates of the new pixel.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
A' (48, 40), B' (48, 100), C' (144, 140), D' (144, 80), and E' (96, 80)
Hexagon ABCDEF is the outline of a figure on a computer screen. The pixels representing the vertices of the pentagon are shown below.
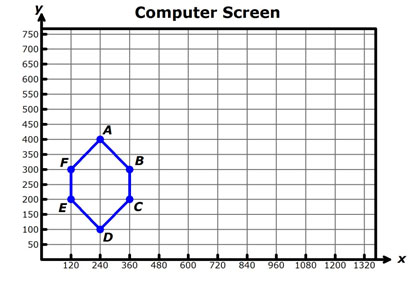
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Use the points to read the coordinates of each labeled point, and then use the scale factor to determine the coordinates of the new pixel. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
A' (420, 700), B' (630, 525), C' (630, 350), D' (420, 175), E' (210, 350), and F' (210, 525)
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
A' (420, 700), B' (630, 525), C' (630, 350), D' (420, 175), E' (210, 350), and F' (210, 525)

Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Use the points to read the coordinates of each labeled point, and then use the scale factor to determine the coordinates of the new pixel. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
No. The coordinates of the new pixel represented by A' will be (540, 900), and 900 in the vertical direction is above the top of the screen, which is 768 pixels high.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
No. The coordinates of the new pixel represented by A' will be (540, 900), and 900 in the vertical direction is above the top of the screen, which is 768 pixels high.
