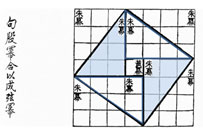
Most mathematicians believe that the Chinese were one of the first civilizations to observe the relationship known today as the Pythagorean Theorem.
The relationship among the side lengths of right triangles was found to be of such high importance that several cultures took the time to study it and put it to use. Today, we call this relationship the Pythagorean Theorem.

Most mathematicians believe that the Chinese were one of the first civilizations to observe the relationship known today as the Pythagorean Theorem.
It is also said that Mayans, Indians, and Egyptians used the Pythagorean Theorem to construct their buildings and pyramids.

However, Greek mathematicians, including Pythagoras, were the first Western mathematicians to record the Pythagorean Theorem. Euclid, an ancient Greek mathematician, used triangles to prove the Pythagorean Theorem to be true.
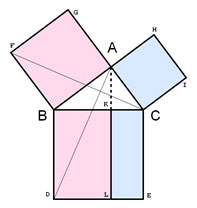
In this lesson, you will examine different ways to represent the Pythagorean Theorem. As you do so, you will need to keep the following vocabulary terms in mind:
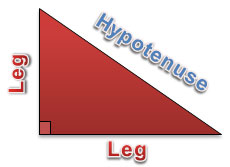
A right triangle has two legs, which are the sides adjacent to the right angle. The third side, which is opposite the right angle, is called the hypotenuse.
Sources of images used in this section as they appear, top to bottom: