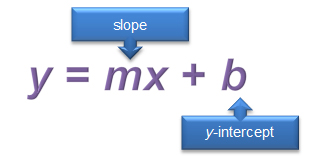
In this section, you will review how to graph lines in slope-intercept form. Recall that slope-intercept form of a linear equation is an equation in which the constants m and b represent the slope and y-coordinate of the y-intercept, respectively.
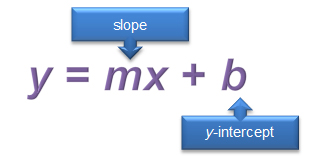
![]() Use the interactive below to investigate how to graph a line when the equation is in slope-intercept form. As you do, notice how the red points change. Also, notice how the vertical and horizontal distances change.
Use the interactive below to investigate how to graph a line when the equation is in slope-intercept form. As you do, notice how the red points change. Also, notice how the vertical and horizontal distances change.
Use the sliders to adjust the values of m and b for a line that is graphed in y = mx + b, or slope-intercept, form.
OnTRACK for College Readiness, Created with GeoGebra
Use the interactive to answer the questions below.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The value of b is equal to the y-coordinate of the y-intercept.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The x-coordinate is 1, which is the denominator of the slope, m. The y-coordinate is the value of b plus the numerator of the slope, m.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The x-coordinate of the right-hand point is the x-coordinate of the middle point plus the denominator of the slope, m. The y-coordinate of the right-hand point is the y-coordinate of the middle point plus the numerator of the slope, m.
The y-intercept of a line is sometimes called the starting point. When graphing a line whose equation is given in slope-intercept form, why do you think that is the case?

Once you have the y-intercept plotted, how can you use the slope to obtain additional points?
Graph each of the following lines. Use an online graphing utility or graph paper and a pencil.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Start with the y-intercept, and then use the slope to locate at least two more points. The numerator of the slope tells you how many vertical spaces to count, and the denominator of the slope tells you how many horizontal spaces to count.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Start with the y-intercept, and then use the slope to locate at least two more points. Rewrite the slope as a fraction. The numerator of the slope tells you how many vertical spaces to count, and the denominator of the slope tells you how many horizontal spaces to count.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Start with the y-intercept, and then use the slope to locate at least two more points. The numerator of the slope tells you how many vertical spaces to count, and the denominator of the slope tells you how many horizontal spaces to count.