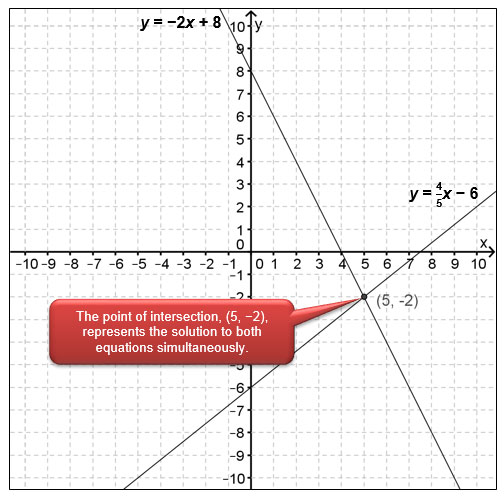
In this lesson, you applied what you had previously learned about graphing linear equations in slope-intercept form to simultaneous linear equations.
When two linear equations are graphed together, they may or may not intersect. (Sometimes, they are parallel!) If they do intersect, then the point of intersection describes the values of x and y that satisfy both equations at the same time. The coordinates of the point of intersection represent the solution to both linear equations simultaneously.
