
Source: We can do it, National Archives

Source: We can do it, National Archives
Mobilization for World War II brought about the end of the Great Depression. As Americans prepared to enter the war, the economy immediately shifted from a consumer production to a war equipment production. In Texas, people moved from rural to urban areas in search of new job opportunities. Manufacturers began to produce goods that could be used in the war effort. Texas served as an important location to the war effort in several ways: Texans planted victory gardens, rationed food, and recycled items like most Americans did during World War II. Texas had specific importance to the war effort.
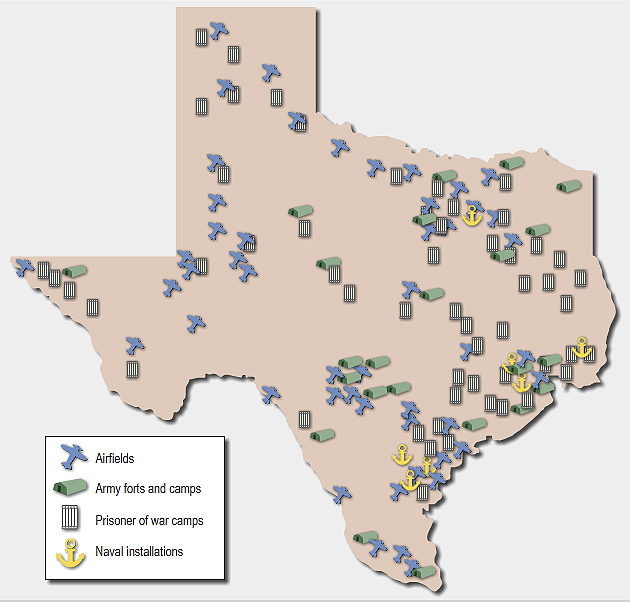
According to the Texas Historical Commission, Texas was home to 175 major military installations, plus numerous minor ones, including 65 Army airfields, 35 Army forts and camps, and seven naval stations and bases. There were also more than 60 base and branch prisoner of war camps; more than in any other state and three internment camps used for the detention of individuals, mostly of Axis nationalities, suspected of being security threats.

Source: B-24 Liberator Consolidated-Vultee Plant, Fort Worth Texas, Signaleer, Wikimedia
Factories that created war products also provided opportunities for minorities and women. The B-24 Liberator airplane was assembled in Fort Worth. Women worked on the assembly line, as did minorities. These marginalized groups were able to take high-waged positions that would normally have been denied to them.
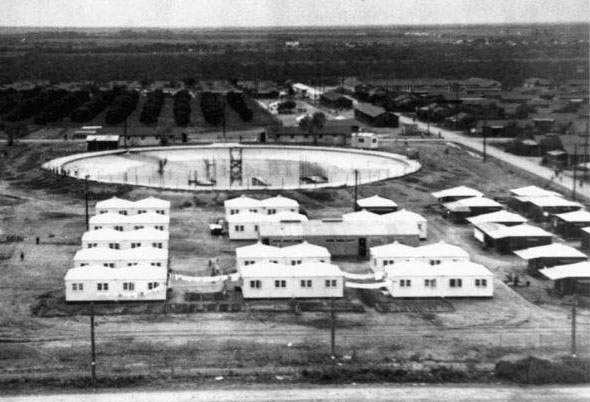

Source: Victory Huts at Crystal City, Texas Historical Commission
There were three internment camps where individuals who were considered security threats were held. The people housed there were often of the nationalities of the Axis Powers.
![]() Watch the video below to learn more about Crystal City’s internment camp, and then answer the following questions in your notes.
Watch the video below to learn more about Crystal City’s internment camp, and then answer the following questions in your notes.
Source: Crystal City Internment Camp (Texas Country Reporter), YouTube
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The Department of Justice created the camp.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Germans, Japanese, and Italians were detained at the camp.
![]() Along with contributing resources to the war effort, Texans also supplied talented people who served in the war. Click on the names of these individuals to learn more.
Along with contributing resources to the war effort, Texans also supplied talented people who served in the war. Click on the names of these individuals to learn more.
In this lesson, you learned about how the Great Depression impacted the United States and Texas economically, socially, and politically. As the economic crisis hit the United States, Texans were also impacted by the Dust Bowl. The Great Depression lasted for nearly a decade. During that time, there was a global political shift. Countries in Europe and Asia saw a change in leadership, which eventually led to World War II. The United States was dragged into the war after Japan bombed Pearl Harbor. As the United States prepared for war, a shift in the economy helped to end the Great Depression. Texas and Texans played a major role in World War II.
Sources for images used in this interactive, as they appear, top to bottom: