Map
Sometimes charts, maps, and statistics can improve your understanding of events like the Dust Bowl and the Great Depression. Examine the map and answer the questions that follow.
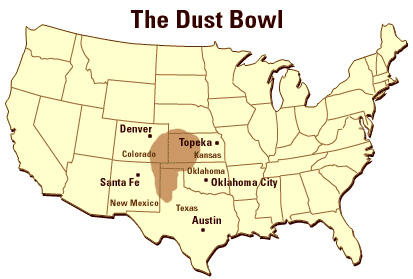
Source: The Dust Bowl, University of Illinois at Urbana.
- What area did the Joads come from if they were called "Okies"?
- Besides crops, what else would farmers raise or grow in the Dust Bowl region?
- Why were these dust storms called “black blizzards”?
Charts and Statistics
Sometimes, instead of a map, a timeline such as the one below is very helpful in understanding “cause and effect” about events that lasted a long time, such as a war or the Dust Bowl. Examine the timeline below and answer the questions that follow in your notes.
Timeline of the Dust Bowl
| YEAR |
EVENT |
EFFECT |
| 1931 |
- Severe drought hits the Great Plains.
- “Black Blizzards” begin.
|
|
| 1933 |
- Farm foreclosures rise.
- Emergency Farm Mortgage Act allots $200 million for refinancing.
Agricultural Administration Act - crops and animals are destroyed to stabilize prices while people starve.
- Workers go on strike in California.
|
Migration to California begins for farmers to seek work.
People object and relief organizations distribute some excess crops and animals. |
| 1934 |
- Drought spreads to cover 75% of country.
- Banks are limited in foreclosures, but too late.
|
More migrant workers go to California. |
| 1935 |
- Emergency Relief Appropriation Act provides $525 million for drought relief.
- April 14 – Black Sunday – worst “black blizzard” of the Dust Bowl occurs, causing extensive damage.
|
Congress declares soil erosion a “national menace” and pays farmers to practice “soil conservation farming”. |
| 1936 |
- LA Police Chief Davis sends policemen to patrol the borders of Arizona and Oregon to keep out “undesirables.”
|
The ACLU sues the city. |
| 1937 |
- FDR begins Shelterbelt Program – planting trees from Canada to Texas to protect the land from erosion.
|
Erosion rates fall. |
| 1938 |
|
|
| 1939 |
- Fall – rain comes finally.
|
The drought ends. |
Answer the following questions about the timeline.
- Why would the government wait so long to do anything about the drought?
- What year did the drought finally end?
- What year did the migration to California begin?
- What three programs did the federal government do to assist farmers like the Joads? Were they successful or not?
- When was the worst “black blizzard?”


