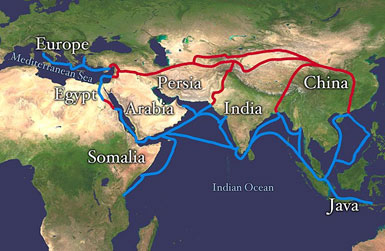

The Silk Road was an example of global trade in ancient history. The Silk Road was an ancient trade route that connected Asia with Europe. Although its primary function was the exchange of goods, the Silk Road also served as an exchange of ideas and cultures. The Silk Road was valuable for the exchange of goods and new products, but one of the most important aspects of the Silk Road was its spread of ideas.

An example of such cultural exchanges occurred with the spread of Buddhism, a religion founded in India. During the first century, Buddhism spread throughout Southeast Asia and into China as a result of trade along the Silk Road. This mural (pictured right), found in the Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves in China, depicts a Central Asian monk teaching an East Asian monk.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required. The Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves are collections of caves used as retreats for Chinese Buddhist monks. The murals depict the interaction between Central Asian and East Asian Buddhist monks.Think about this - What is the significance of painting murals depicting elements of the Buddhist religion?

The historical exchange along the Silk Road is an example of how trade can impact culture. Although today’s global trade may function differently than that of the Silk Road, there are still similarities in its impact.
In this lesson, you will learn about the different ways specific trade agreements have caused cultural changes in specific regions.
Sources for images used in this section, as they appear top to bottom: