![]() Watch this short video and pay attention to the goals, benefits, and governing bodies of the EU. This information will be needed for the remaining activities.
Watch this short video and pay attention to the goals, benefits, and governing bodies of the EU. This information will be needed for the remaining activities.
Source: What is the EU? Mr.MillerProductions, YouTube
With the addition of Romania and Bulgaria, there are now 27 countries in the European union.
Remember that the EU does not have the same type of government as the United States. It is also important to recognize that it does not function like the United Nations. The EU is unique in that the member countries are sovereign and independent nations, but they pool their sovereignty in order to gain a strength and world influence none of them could have on their own.
Here are the main governing bodies of the EU.
The European Parliament:

Source: The European Parliament, Europa
Three main functions of the European Parliament:
The Council of the European Union:

Source: The council of the European Union meeting room, Europa
The Council is the EU's main decision-making body. It represents the member states, and its meetings are attended by one minister from each of the EU's national governments.
The European Commission:

Source: Barroso Commission, Europa
The commission is a 27-member group of men and women from each of the member countries who are appointed to run the institution and take its decisions. The commission members may have all held political positions in their countries of origin and many have been government ministers, but as Members of the Commission they are committed to acting in the interests of the Union as a whole and not taking instructions from national governments.
Along with promoting political stability, the EU also works to address public policy that impacts its citizens. Click on the link below and choose two (2) areas of legislation that the EU is currently addressing (Example: Education, Agriculture, etc.). Research the two areas and determine what policy the EU is forming in these areas). Write your answers in your notes.
As you learned in the beginning of this lesson, the EU is also involved in policy that impacts the world.

![]()
Source: A Duty to Aid, Europa
The EU believes that it should provide humanitarian aid wherever possible. The EU is present in all trouble spots including Iraq, Afghanistan, the Palestinian Territories, and several parts of Africa. Its relief activities are global, sometimes taking place in less publicized areas. These include Chechnya, Kashmir, Nepal, Burma (Myanmar), the Western Sahara and Colombia.
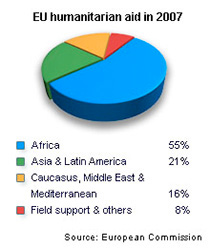
Source: EU Humanitarian Aid in 2007, European commission, Europa

